Custom scripts
Gephi-Lite does not have a plugin marketplace, but it includes a native scripting language: JavaScript. In many places, this lets you write JavaScript code instead of using the standard features.
Nodes/Edges filtering
From the Filters menu, choosing Custom script opens the script editor, allowing you to implement this function:
/**
* Define a custom filter function.
* The function is executed for each node.
* If it returns true, the node is included in the result set; otherwise, it is excluded.
*
* @param {string} id ID of the item
* @param {GraphNode} attributes Attributes of the item
* @param {AbstractGraph<GraphNode, GraphEdge>} graph Graphology instance (https://graphology.github.io/)
* @return {boolean} TRUE if the item should be kept in the graph, FALSE to filter it
*/
function filter(id, attributes, graph) {
//
// Your code goes here
//
return true;
}
Examples
- Keep nodes that have a property 'age' superior than
18:
function filter(id, attributes, graph) {
return attributes.age > 18;
}
- Keep nodes that have a property 'age' below 18 and with a degree inferior to 10 :
function filter(id, attributes, graph) {
return attributes.age < 18 && graph.degree(id) < 10;
}
- Keep nodes on which the property 'job' is defined
function filter(id, attributes, graph) {
return attributes.job !== undefined;
}
Custom layout
In the Layout menu, selecting Custom layout opens the script editor, where you can implement this function:
/**
* Function that returns coordinates for the specified node.
*
* @param {string} id The ID of the node
* @param {GraphNode} attributes Attributes of the node
* @param {number} index The index position of the node in the graph
* @param {AbstractGraph<GraphNode, GraphEdge>} graph The graphology instance (https://graphology.github.io/)
* @returns {x: number, y: number} The computed coordinates of the node
*/
function nodeCoordinates(id, attributes, index, graph) {
//
// Your code goes here
//
return { x: attributes.x, y: attributes.y };
}
Examples
- Random layout on a 1000x1000 space
function nodeCoordinates(id, attributes, index, graph) {
return { x: Math.random() * 1000, y: Math.random() * 1000 };
}
- Circular layout
function nodeCoordinates(id, attributes, index, graph) {
return {
x: Math.cos((index * (Math.PI * 2)) / graph.order) * 500,
y: Math.sin((index * (Math.PI * 2)) / graph.order) * 500,
};
}
Scripted node/edge attribute
On the Data page, choosing Create nodes scripted attribute in the Data creation menu opens the script editor, allowing you to implement this function:
/**
* Function that returns a new attribute value for the specified node/edge.
*
* @param {string} id The ID of the node/edge
* @param {GraphNode} attributes Attributes of the node/edge
* @param {number} index The index position of the node/edge in the graph
* @param {AbstractGraph<GraphNode, GraphEdge>} graph Graphology instance (https://graphology.github.io/)
* @returns number|string|boolean|null|undefined" The value of the new node/edge's attribute
*/
function addAttribute(id, attributes, index, graph) {
//
// Your code goes here
//
return Math.random();
}
Examples
- If you have an attribute named 'valid' which take 0 or 1 and you want to cast it into a boolean
function addAttribute(id, attributes, index, graph) {
return attributes.valid === 1;
}
- If you have attributs named 'firstname' and 'lastname' and you want to concatenate them (usefull for graph label)
function addAttribute(id, attributes, index, graph) {
return (attributes.firstname || "") + " " + (attributes.lastname || ");
}
Script editor
The script editor is displayed in a modal.
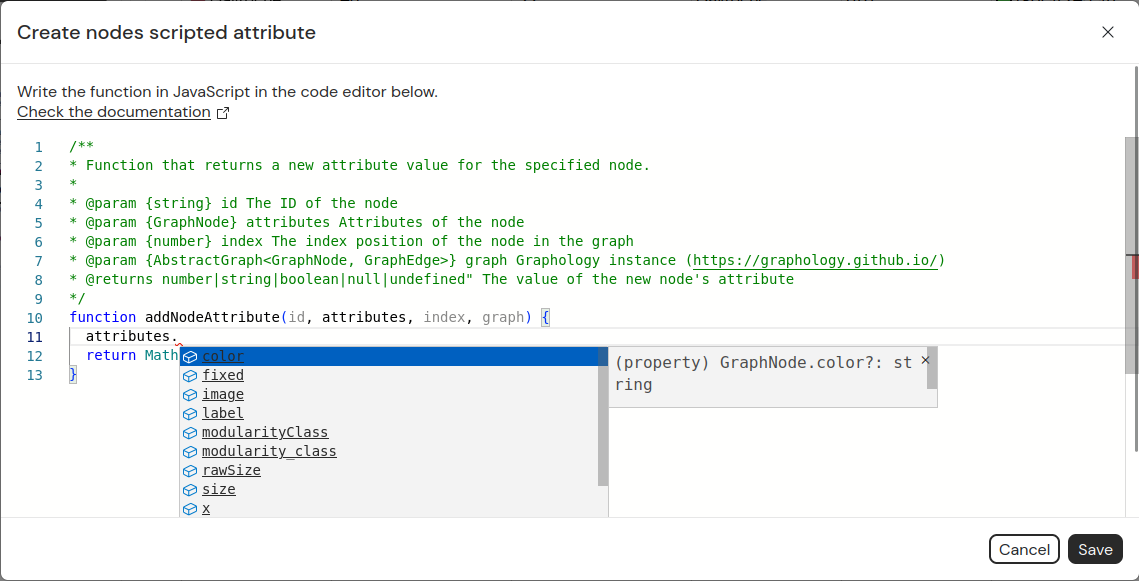
The editor is based on Monaco, so if you use VS Code, it should feel familiar.
Types are defined for each function parameter (such as attributes or graph), enabling autocompletion.